欢迎访问西华大学-食品与生物工程学院!2024年06月12日11时53分56秒




近日,西华大学食品与生物工程学院 “农产品贮藏与加工”团队在International Journal of Biological Macromolecules(一区,IF: 8.2)上发表题为“Multi-scale structural characteristics ofblack Tartary buckwheat resistant starch by autoclaving combined with debranching modification”的研究论文。西华大学2021级硕士研究生郑发英为论文第一作者,邢亚阁教授为论文通讯作者。该研究工作得到了成都市科技项目(2022-YF05-00914-SN)和四川省科技计划项目(2018NZ0097)的资助。

降低淀粉的消化率有利于维持餐后血糖平衡,对预防慢性疾病有独特的益处。根据消化速度,淀粉及其衍生物可进一步分为快速消化淀粉、慢速消化淀粉或抗性淀粉(RS)。抗性淀粉具有与膳食纤维类似的功能,包括降血糖、抑制体内脂肪堆积和减少癌症患病等。RS 可通过改变下丘脑食欲中枢的神经元活动来影响食欲调节和饱腹感。在酶水解淀粉的过程中,酶需要扩散并与淀粉底物结合,然后进一步水解糖苷键。因此,可以想象酶在底物中的扩散和吸收速度在很大程度上影响着淀粉的消化速度。一般来说,淀粉的消化率受其多尺度结构的影响,如颗粒结构(1-100 μm)、结晶和片层结构(约10 nm)以及分子结构(约0.1 nm)。尽管高压糊化或高压糊化-脱枝处理在抗性淀粉的制备过程中被广泛使用,但它们对抗性淀粉的多尺度结构的影响以及与淀粉消化的关系仍不清楚。本研究通过分析高压糊化和高压糊化-脱枝联合处理对抗性淀粉多尺度结构的影响,研究了黑苦荞抗性淀粉的多尺度结构与其消化率之间的关系。

Fig. 1. Resistant starch content of BTBNS, CBNS, BRS-AC and BRS-ACP starches. BTBNS, black Tartary buckwheat native starch; CBNS, common buckwheat native starch; BRS-AC, black Tartary buckwheat resistant starch subjected to autoclaving treatment; BRS-ACP, black Tartary buckwheat resistant starch subjected to autoclaving-pullulanase combined treatment.
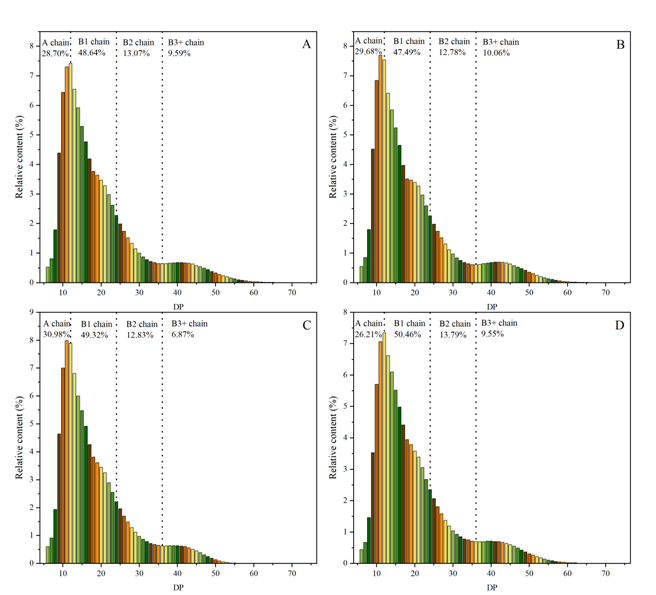
Fig. 2. chain length distributions of BTBNS, CBNS, BRS-AC and BRS-ACP starches. A, BTBNS, black Tartary buckwheat native starch; B, CBNS, common buckwheat native starch; C, BRS-AC, black Tartary buckwheat resistant starch subjected to autoclaving treatment; D, BRS-ACP, black Tartary buckwheat resistant starch subjected to autoclaving-pullulanase combined treatment. A chain, the rate of DP range from 6-12 in chain length distributions; B1 chain, the rate of DP range from 13-24 in chain length distributions; B2 chain, the rate of DP range from 25-36 in chain length distributions; B3+ chain, rate of DP ≥ 37 in chain length distribution; DP, average degree of polymerization.
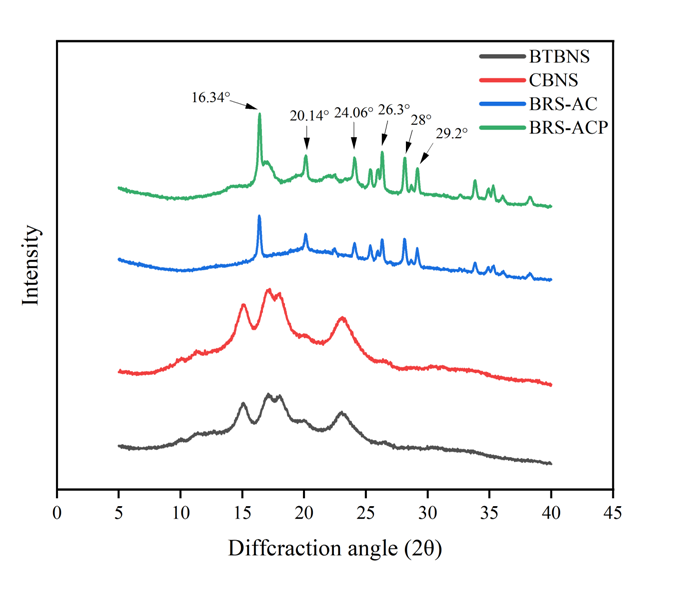
Fig. 3. XRD patterns of BTBNS, CBNS, BRS-AC and BRS-ACP starches. BTBNS, black Tartary buckwheat native starch; CBNS, common buckwheat native starch; BRS-AC, black Tartary buckwheat resistant starch subjected to autoclaving treatment; BRS-ACP, black Tartarybuckwheat resistant starch subjected to autoclaving-pullulanase combined treatment.
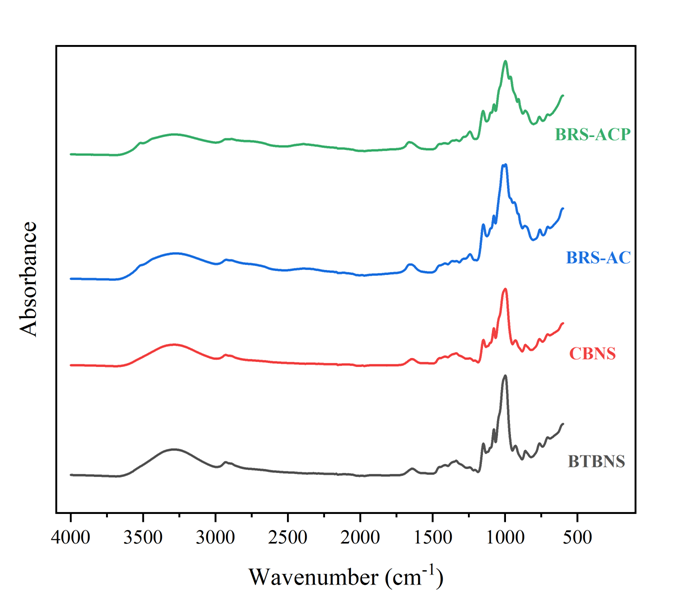
Fig. 4. Deconvoluted ATR-FTIR spectra of BTBNS, CBNS, BRS-AC and BRS-ACP starches.BTBNS, black Tartary buckwheat native starch; CBNS, common buckwheat native starch;BRS-AC, black Tartary buckwheat resistant starch subjected to autoclaving treatment; BRS-ACP, black Tartary buckwheat resistant starch subjected to autoclaving-pullulanase combined treatment.
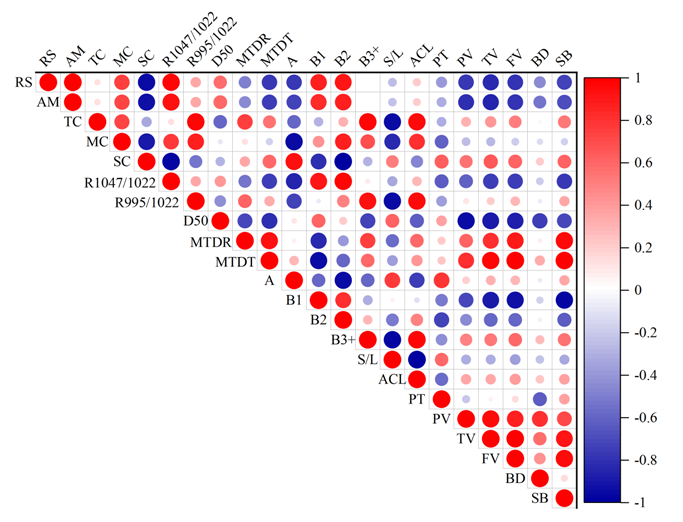
Fig. 5. Pearson correlation analysis of BTBNS, CBNS, BRS-AC and BRS-ACP starches. BTBNS, black Tartary buckwheat native starch; CBNS, common buckwheat native starch; BRS-AC, black Tartary buckwheat resistant starch subjected to autoclaving treatment; BRS-ACP, black Tartary buckwheat resistant starch subjected to autoclaving-pullulanase combined treatment. RS, resistant content; AM, Amylose content; TC, total crystallinity; MC, micro-crystalline; SC, sub-crystalline; R1047/ 1022, the ratios of absorbance of native and resistant starch at 1047 and 1022 cm-1 of ATR-FTIR; R995/1022, the ratios of absorbance of native and resistant starch at 995 and 1022 cm-1 of ATR-FTIR; D50, median particle size; MTDR, maximum thermal degradation rate; MTDT, maximum thermal degradation temperature; A, the rate of DP range from 6 to 12 in chain length distributions; B1, the rate of DP range from 13 to 24 in chain length distributions; B2, the rate of DP range from 25 to 36 in chain length distributions; B3+, rate of DP ≥ 37 in chain length distribution; S/L, short/long chain in branch chain-length distributions. BD, branching degree in chain length distribution; ACL, average Chain length; PT, peak time; PV, peak viscosity; TV, trough viscosity; FV, final viscosity; SB, setback.
原文链接
邢亚阁,西华大学食品与生物工程学院教授,硕士生导师,第十二批四川省学术和技术带头人后备人选,九三学社西华大学委员会主任委员,2015.11-2016.11加拿大圭尔夫大学访问学者。科技部三区服务专家,西华大学首批“青年学者”,西华大学首批“唐立新优秀学者”。长期从事“食品工厂设计”、“食品质量与安全”、“技术经济学(食品)”、“食品物性学”等多门课程授课工作。发表SCI收录英文文章40余篇,授权国家发明专利20余项。主持参与国家、省部级、市级和企业委托项目30余项,获四川省科技进步二等奖1项、天津市科技进步二等奖2项、四川省科技进步三等奖2项,完成省级鉴定成果或评价10余项。
郑发英,西华大学食品与生物工程学院2021级硕士研究生。硕士研究方向为食品工程。硕士期间,共发表3篇SCI论文,获得研究生一等学业奖学金1次和三等学业奖学金1次。
责编:梁珂静
地址:中国·四川·成都·西华大学·第五教学楼D区
邮编:610039
电话:028-87720552
传真:028-87720552

官方微信